No Products in the Cart
Picture trying to perform delicate surgery in the middle of a dust storm. It sounds impossible, right? That’s pretty much what welding or working with sensitive materials is like without a protective shield. Using argon als schutzgas (argon as a shielding gas) creates an invisible, ultra-pure bubble that fences off the work area from contamination, ensuring every job is done with precision and quality.

In any high-temperature metal process, the surrounding air is the enemy. The atmosphere is full of reactive gases—mainly oxygen and nitrogen—that are just waiting to combine with molten metal. This reaction, known as oxidation, can completely ruin a weld, introduce tiny defects, and contaminate sensitive materials. The result? Brittle joints and costly, catastrophic failures.
This is where argon steps in. It acts as an invisible bodyguard for the work area. By flooding the process zone, argon physically pushes out the harmful atmospheric gases. It creates a pure, controlled environment where metals can be joined or processed exactly as intended.
So, what makes argon so good at this job? Its power comes from a unique combination of physical and chemical properties that make it the ideal guardian for sensitive industrial tasks. Getting to know these characteristics is the first step to understanding why argon is so indispensable.
Here's what makes it stand out:
Argon’s effectiveness isn't just theoretical. Its ability to shield against atmospheric contamination is the very foundation of quality control in sectors from aerospace engineering to electronics manufacturing, where even microscopic impurities can lead to catastrophic failures.
A consistent, reliable supply of argon is the backbone of these critical operations. This invisible shield is what allows industries to achieve the highest standards of quality, precision, and safety day in and day out.
To really get why argon als schutzgas is the go-to choice for so many critical jobs, we need to look at what makes it tick. It’s not just a random gas from a cylinder; its effectiveness is baked right into its atomic structure and physical nature. These traits make argon the perfect invisible guardian for sensitive, high-temperature processes.
At its core, argon is a noble gas. Think of the noble gases as the reclusive VIPs of the periodic table—they’re chemically stable and don't mingle with other elements. This is all down to their outermost electron shell being completely full, which means they have zero interest in reacting. Even when faced with the intense heat of a welding arc, argon stays inert, refusing to form compounds that could ruin the work.
One of argon’s most useful tricks is its density. It’s about 40% heavier than the air we breathe. That simple fact makes a huge difference in how well it can shield a workpiece.
Picture pouring a thick syrup onto a plate; it sinks, settles, and shoves lighter liquids like water out of the way. Argon does the exact same thing in gas form. When it flows from a welding torch or fills a chamber, it naturally sinks and displaces the lighter, reactive gases in the atmosphere like oxygen and nitrogen. This creates a stable, dense, and protective blanket right where you need it most, effectively walling off the molten metal from contamination.
It's simple physics: Argon's greater density isn’t just a minor detail—it’s the primary reason it forms such a consistent, robust, and undisturbed shield over the critical work zone, preventing costly defects.
To put its physical properties into perspective, let's compare argon to the two most abundant gases in our atmosphere.
Argon Properties vs. Common Atmospheric Gases
| Property | Argon (Ar) | Nitrogen (N₂) | Oxygen (O₂) | Significance in Shielding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic Mass (amu) | 39.95 | 28.01 | 32.00 | Heavier than air, enabling it to displace oxygen and nitrogen effectively. |
| Density (at STP) | 1.784 g/L | 1.251 g/L | 1.429 g/L | Its higher density creates the "heavy blanket" that settles over the work area. |
| Chemical Reactivity | Inert | Reactive at high temps | Highly reactive | Argon won't combine with the molten metal, preventing oxides and nitrides. |
| Ionisation Potential | Low | High | High | Requires less energy to start and maintain a stable electrical arc. |
As the table shows, argon's combination of weight and inertness gives it a clear advantage over the very gases it's designed to protect against.
Beyond being heavy and non-reactive, argon has another ace up its sleeve: a low ionisation potential. In plain English, this means it takes very little energy to create a stable electrical arc—the heart and soul of processes like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding.
This quality allows electricity to flow smoothly and consistently from the electrode to the workpiece. What you get is a highly stable, focused arc that’s much easier for an operator to control. This stability leads to less spatter, better heat transfer, and ultimately, cleaner, stronger, and more precise welds. It's this perfect storm of chemical aloofness, physical weight, and electrical stability that makes argon the superior shielding gas for so many demanding jobs.
From the controlled chaos of an automotive production line to the sterile quiet of a research lab, argon’s role as a protective shield is a common thread in modern innovation. Its unique properties make it a silent, indispensable workhorse across Germany's most important industrial sectors. The gas guarantees that processes demanding absolute purity and stability can run smoothly, without any unwanted atmospheric meddling.
The most recognisable application for argon als schutzgas is, without a doubt, in welding. It’s the gold standard for high-precision techniques like Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) and Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, particularly when you’re working with tricky non-ferrous or reactive metals.
Think about welding materials like aluminium, stainless steel, or titanium. At the scorching temperatures of the welding arc, even the tiniest bit of oxygen can spell disaster for the finished product. Argon creates a dense, inert bubble right around the weld pool, physically blocking out atmospheric gases and stopping oxides and nitrides from ever forming. This invisible shield is what ensures a perfect, high-integrity weld that’s both strong and clean.
But argon's job doesn't stop at traditional fabrication. It's also a critical player in additive manufacturing, what many know as metal 3D printing. In a process like Selective Laser Melting (SLM), a powerful laser fuses fine metal powders together, layer by painstaking layer. This has to happen in a perfectly inert atmosphere to keep the microscopic powder particles from oxidising, which would completely wreck the final part's structural integrity.
To prevent this, argon floods the build chamber. This creates the pristine environment needed to produce incredibly complex and precise metal parts for aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. It ensures every layer fuses perfectly, creating components with mechanical properties that were once impossible to achieve.
This need for pure, controlled environments extends deep into the world of scientific research. In labs all over Germany, argon is essential for a variety of delicate tasks.
Here in Germany, argon has solidified its place as one of the most important shielding gases, propping up key sectors like automotive manufacturing and mechanical engineering. The market reflects this; the German argon gas market was valued at around USD 893.6 million in 2024 and is expected to climb to USD 1.64 billion by 2033. This growth is a direct result of Germany's powerful industrial base, where argon is non-negotiable for preventing oxidation in weld pools and heat-affected zones. You can find more insights into the German argon market over at reedintelligence.com.
Argon isn't just another welding gas; it's an enabling technology. It provides the invisible shield that allows us to create everything from stronger car frames and intricate 3D-printed jet engine parts to breakthroughs in chemical synthesis.
Whether it’s on the factory floor or in a high-tech lab, argon's inert presence is the common denominator linking quality, precision, and innovation. Its sheer versatility and reliability make it a cornerstone of both industrial production and scientific progress, cementing its status as an essential resource for any operation where perfection is the only standard.
Picking the right argon als schutzgas is a bit more involved than just grabbing the first cylinder you see. Not all argon is the same, and the difference between a flawless weld and a failed part often boils down to purity levels and the right gas mix. It's really about matching the gas to your specific job, balancing what you need for top performance against what makes sense for your budget.
For most day-to-day industrial welding, a standard purity grade will do the job perfectly, giving you great protection. But when you’re talking about high-stakes work, like making semiconductors or in advanced scientific research, only ultra-high purity argon will cut it. In those settings, even the tiniest impurity can cause a major defect.
You'll see argon purity classified with a grade, like Grade 4.8 or Grade 5.0. This number isn’t just jargon; it’s a quick way to know exactly how pure the gas is.
For instance, Grade 5.0 argon is 99.999% pure. This is the super-clean stuff, essential for applications where even the slightest reaction could ruin the entire process. On the other hand, standard industrial argon is often around Grade 4.6 (99.996% pure), which provides solid protection for most TIG and MIG welding on materials like stainless steel and aluminium without the extra cost.
The key isn't to always buy the highest purity available. It's about understanding how sensitive your process is to contamination. Paying for purity you don't need is just a waste of money, but skimping on it can lead to costly rework and failed materials.
The flowchart below gives a good overview of where argon’s protective qualities are most critical.
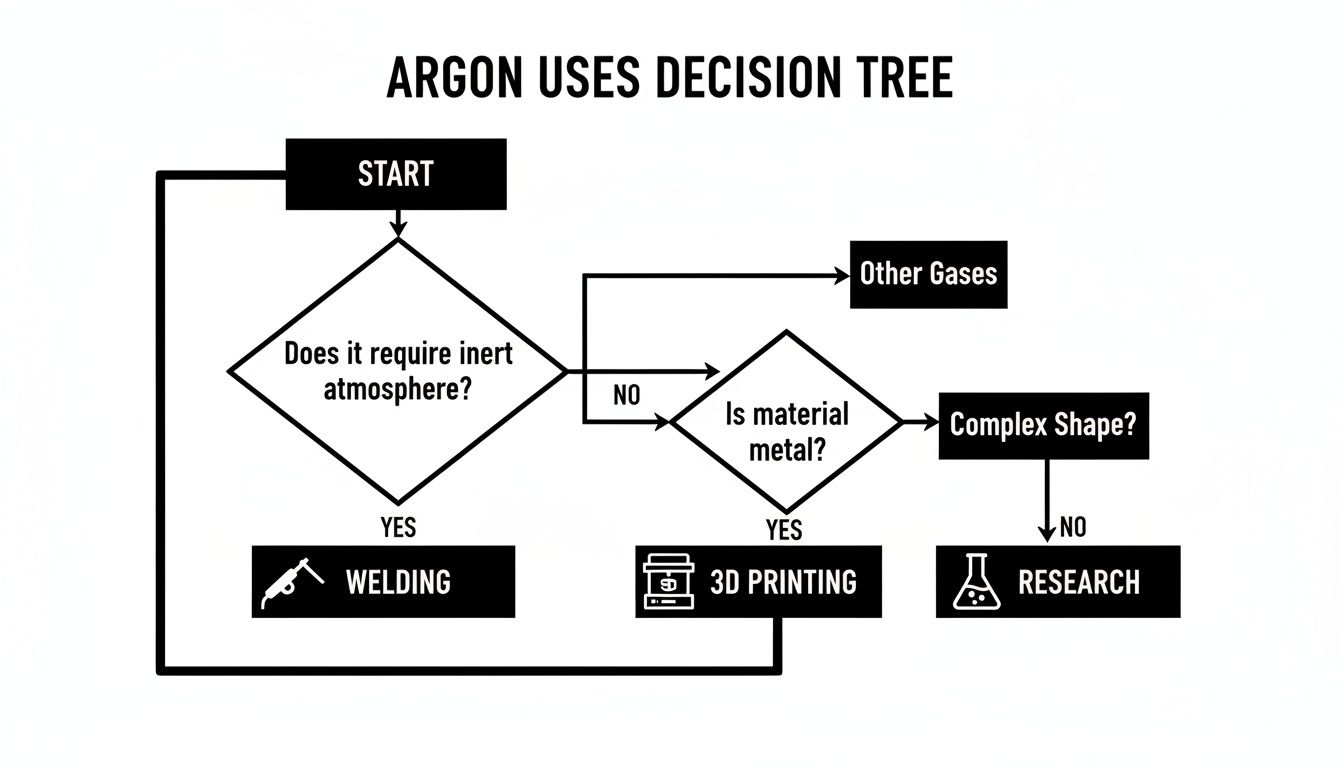
As you can see, argon is a cornerstone shielding gas, supporting everything from basic welding jobs to the most advanced manufacturing and research.
While pure argon is the champion for many non-ferrous metals, mixing it with other gases can really enhance its performance, especially when you're welding steel. These blends are specifically engineered to tweak the welding arc’s behaviour. If you want to dive deeper, our detailed guide offers more insights on the best TIG welding gas for various materials.
The table below breaks down some of the most common argon-based blends, showing you what they're made of and where they shine. Think of it as a quick reference for matching the right mix to your project.
| Gas Mixture | Typical Composition | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ar/CO₂ | Argon + 5-25% Carbon Dioxide | MIG welding of carbon and low-alloy steels | Increases penetration and arc stability, resulting in a cleaner bead profile. A true workhorse for steel fabrication. |
| Ar/He | Argon + 25-75% Helium | TIG/MIG welding of thick aluminium & copper | Produces a much hotter arc, essential for materials that rapidly dissipate heat. Great for heavy-duty jobs. |
| Ar/O₂ | Argon + 1-2% Oxygen | MIG welding of stainless and carbon steels | Improves weld pool fluidity and arc stability, leading to a smoother, flatter weld finish with less spatter. |
Each of these mixtures is designed to solve a specific challenge, whether it's getting more heat into a thick plate or achieving a perfect finish on stainless steel.
At the end of the day, your choice comes down to the material you’re working with, its thickness, the welding process you’re using, and the final look you want to achieve. Getting a handle on these factors is how you pick the perfect argon purity or mixture to get the job done right, every single time.

While argon is non-toxic and non-flammable, you can't afford to get complacent. Its physical properties demand strict safety protocols, whether you're dealing with high-pressure gas cylinders or cryogenic liquid. Getting this wrong can lead to serious workplace incidents. Mastering safe handling and adopting modern storage solutions isn't just about ticking compliance boxes; it's fundamental to protecting your team and keeping operations running smoothly.
The biggest threat from gaseous argon als schutzgas is simple: asphyxiation. Argon is heavier than air and has no smell, so a leak in a poorly ventilated room can quietly push out all the oxygen to dangerously low levels. This is why proper ventilation and reliable oxygen monitoring systems are non-negotiable in any enclosed space where argon is stored or used.
Liquid argon introduces a dual threat. First, its bone-chillingly low temperature of -185.9°C will cause severe cryogenic burns the instant it touches skin. Second, a small spill isn't a small problem. Liquid argon expands into a massive volume of gas—about 840 times its liquid volume—massively increasing the risk of oxygen displacement in confined spaces.
Handling liquid argon demands specialised personal protective equipment (PPE). This is not optional. Cryogenic gloves, safety goggles or a full-face shield, and proper footwear are the absolute minimum to prevent life-altering injuries.
To manage these risks, every facility needs a clear and enforced set of safety rules.
For any facility with high gas consumption, juggling dozens of individual high-pressure cylinders is a logistical headache. It’s inefficient and multiplies the risks that come with frequent handling. Modern cryogenic storage systems, like micro-bulk tanks and liquid cylinders (dewars), offer a much safer and more cost-effective way forward.
These systems store argon in its dense liquid form, dramatically reducing your facility's storage footprint and the daily grind of cylinder change-outs. A single on-site micro-bulk tank can replace hundreds of conventional cylinders, which means far less manual handling and fewer potential leak points.
This shift reflects a broader trend in the German industrial gas market. For supplying argon als schutzgas, the logistics increasingly favour liquid delivery. In fact, liquid argon is projected to hold the largest market share in the years to come simply because its density makes storage and transport more efficient and less costly. Large industrial sites, like German automotive plants, often have liquid argon delivered to insulated tanks. It's then vaporised on-site to feed shielding-gas manifolds, a system that cuts down on cylinder management and eliminates production downtime. You can learn more about the strategic importance of liquid argon in Germany.
Making the right call on your argon supply can have a huge impact on your bottom line and how smoothly your operation runs. It's about more than just ordering gas; a smart strategy matches your supply mode to your actual consumption. This is how you guarantee a reliable, safe, and cost-effective flow of argon als schutzgas where you need it most.
For anyone using argon in low volumes or only now and then, the classic high-pressure gas cylinders are still a perfectly practical choice. They give you flexibility without a big upfront investment, which is ideal for smaller workshops, mobile repair outfits, or labs with modest needs.
But as your argon consumption ramps up, juggling a large fleet of individual cylinders starts to get old, fast. It becomes inefficient and expensive. Constantly swapping out empty cylinders kills workflow, and the paperwork involved in tracking and reordering them really starts to add up.
This is the point where switching to liquid argon storage becomes a total game-changer. Liquid dewars are a solid step up from cylinders, giving you a lot more gas in a much smaller footprint. For facilities with serious, consistent demand, micro-bulk or full-scale bulk tanks are hands-down the most economical and efficient way to go.
These systems bring some serious advantages to the table:
Choosing a supply mode isn't just a procurement task; it's a critical business decision. The right system pays for itself through better uptime, lower labour costs, and a much smoother supply chain, freeing up your team to focus on what they do best.
Who you buy your gas from is just as important as how you store it. A truly dependable partner does more than just drop off gas; they provide a complete solution. This means expert advice to figure out the best storage system for you, professional installation, ongoing maintenance, and rock-solid logistics so you never have to worry about running out. Our guide on the pros and cons of buying or renting gas cylinders offers some more valuable perspective on these decisions.
Within Germany's wider compressed gas market, argon als schutzgas is a specialised but fast-growing corner. The total German market for compressed gas brought in USD 291.4 million in 2024 and is projected to climb to USD 379.2 million by 2030. While other gases might have bigger market shares overall, argon is the top gas by value in the welding world. It's also expected to grow faster than its peers, which really underscores its industrial importance.
Got a few more questions? Let's clear up some common points about working with argon.
Nope, argon is completely inert. This means it won’t catch fire and it isn't poisonous.
The real danger with argon is simple displacement. It's heavier than air, so in a closed-off space, it can literally push the breathable oxygen out of the room, creating a serious suffocation hazard. That's why good ventilation is non-negotiable when you're working with argon als schutzgas.
It really comes down to how much of it is available in the air around us. The atmosphere is only about 0.93% argon, while it's packed with roughly 78% nitrogen.
Pulling that tiny fraction of argon out of the air requires a complex, energy-hungry process called cryogenic air separation. That intensive production process is what makes it pricier than more common industrial gases.
That depends entirely on how you're welding it. For TIG welding any kind of steel, pure argon is the gold standard. It gives you a beautifully clean and stable arc, which is exactly what you want for precise TIG work.
But for MIG welding steel, pure argon is a poor choice; you'll likely struggle with an unstable, messy arc. A mix of argon and CO₂ is a much better option for MIG, giving you the performance and bead quality you're looking for.
For state-of-the-art cryogenic storage solutions that ensure a safe and reliable supply of argon and other industrial gases, trust Cryonos GmbH. Explore our advanced micro-bulk systems and liquid cylinders at https://www.cryonos.shop.