No Products in the Cart
A Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch, more commonly known as a medical oxygen pressure regulator, is the critical piece of safety hardware that connects a high-pressure oxygen cylinder to either a patient or a piece of sensitive equipment. Its entire job is to take the immense pressure coming out of the tank—often well over 200 bar—and step it down to a safe, usable, and incredibly precise low-pressure flow. This is what ensures a gentle, therapeutic delivery of oxygen.
Think of a massive dam holding back a powerful reservoir. The dam's gates don't just swing wide open; they're designed to release a controlled, steady stream of water. A medical oxygen pressure regulator operates on the exact same principle. It effectively tames the raw, immense power of compressed oxygen, converting it into a gentle, life-sustaining flow that’s safe for a patient to breathe or for use in delicate lab work.
Without this crucial device, trying to use oxygen straight from a cylinder would be dangerously forceful—completely unusable and unsafe.

This level of precision is absolutely non-negotiable in settings where accuracy and safety are everything. In a hospital, it guarantees that a patient receives the exact prescribed dosage, protecting their fragile respiratory system. But the role of a high-quality Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch goes far beyond the hospital bedside.
In highly advanced scientific and medical fields, the need for exact gas control is just as critical. Just think about these scenarios:
In essence, a medical oxygen regulator is a guardian of pressure. It stands between the volatile potential of a high-pressure cylinder and the delicate requirements of a patient or a scientific procedure, guaranteeing safety, control, and reliability.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about these essential devices. We’ll break down their core components, help you decode the technical specifications, and cover the best practices for choosing and maintaining them. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how to select and operate a Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch for maximum efficiency and unwavering safety in your specific application.
To really get a feel for how a Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch (medical oxygen pressure reducer) works, you have to look under the hood. It’s less like a single object and more like a finely tuned team of components, all working together to safely wrangle high-pressure oxygen and deliver it with precision. Each part has a very specific, critical job to do.
Think about it: the whole point is to tame an immense amount of force. The process kicks off at the inlet connection, which is the heavy-duty fitting that securely latches the regulator onto the oxygen cylinder. This connection has to be absolutely perfect to prevent any dangerous leaks. From there, the internal guts of the device get to work, stepping that pressure way down to a level that’s safe and usable for medical applications.

Visual feedback is everything. That's why every regulator has two pressure gauges giving you instant, vital information. One gauge shows the high pressure left inside the oxygen cylinder—your fuel gauge, essentially. The second one displays the reduced, outgoing pressure that’s actually being delivered to the patient or equipment. Simple, but critical.
The user's main point of interaction is the flowmeter. This is usually a knob or dial that lets you precisely set the oxygen delivery rate in litres per minute (LPM). This is what allows clinicians to tailor the therapy to each patient's exact needs. And, of course, there’s a non-negotiable safety feature: the safety relief valve. If anything goes wrong internally and pressure spikes, this valve automatically vents the excess, preventing a catastrophic failure.
Internally, not all regulators are created equal. The two most common designs you'll run into are piston-style and diaphragm-style, and each has its place.
The COVID-19 pandemic threw the importance of reliable gas supply systems into sharp relief, with demand for medical gases jumping by 40-50% in 2020-2021. This really highlighted the need for dependable cryogenic solutions like the Liquid Cylinders and AC Micro Bulk systems from Cryonos GmbH, which ensure biobanks and pharmaceutical labs never run dry. You can dig deeper into this market shift and its impact on medical gas supply.
Beyond the core mechanism, regulators are also defined by how they reduce pressure. Choosing between a single-stage and two-stage model comes down to how stable you need that pressure to be.
A single-stage regulator does the job in one go, dropping the high cylinder pressure down to the delivery pressure in a single step. They're straightforward and cost-effective. The catch? As the pressure inside the cylinder drops, the outlet pressure can creep up slightly. It’s a known phenomenon called the "supply pressure effect."
For any application where absolute, unwavering consistency is non-negotiable, a two-stage regulator is the only way to go. It’s like having two regulators built into one, giving you an exceptionally stable output pressure from a full tank all the way to empty.
A two-stage regulator, on the other hand, breaks the process into two steps. The first stage knocks the high cylinder pressure down to a more manageable intermediate level. The second stage then refines that down to the final, precise output pressure. This two-step process completely isolates the output from any pressure drops in the cylinder. That makes it indispensable for long-term patient care, sensitive anaesthesia equipment, and scientific experiments where even a tiny fluctuation in flow could ruin your results.
Choosing the right Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch (medical oxygen pressure regulator) means looking under the bonnet and getting to grips with its technical heart. These specifications aren't just random numbers on a data sheet; they're the critical details that define how the device performs, how safe it is, and whether it's the right fit for your job. Getting this right is non-negotiable.
Think of it like picking an engine for a vehicle. A nippy little city car needs something completely different from a massive lorry hauling heavy goods. In the same way, a regulator for a portable oxygen cylinder has totally different technical demands than one hooked up to high-precision lab equipment.
At its most basic, three key numbers tell you almost everything you need to know about what a regulator can do.
First up is inlet pressure. This is the maximum pressure the device can safely take from the oxygen cylinder it's attached to. For the vast majority of medical and technical gas cylinders here in Europe, that pressure is a standardised 200 bar. The regulator has to be built tough enough to handle that immense force day in and day out.
Next, you have the outlet pressure, which is the reduced, usable pressure the regulator delivers downstream. This is usually adjustable within a certain range, like 0-10 bar, letting you dial in the exact pressure needed for specific tools or clinical applications.
Finally, there's the flow rate. This tells you how much oxygen is being delivered over time, measured in litres per minute (LPM). Medical regulators often have very clear, stepped settings to ensure dosages are precise and repeatable for patient therapy.
The real magic is in how these three specs—inlet pressure, outlet pressure, and flow rate—work together. If there's a mismatch between what the regulator can do and what your application needs, you're looking at poor performance at best, and a serious safety risk at worst.
To make these concepts clearer, here’s a quick overview of the key specifications you’ll encounter:
Medical Oxygen Regulator Specifications Overview
| Parameter | Typical Range / Standard | Importance for Users |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet Pressure | 200 bar (up to 300 bar for some industrial cylinders) | Must match the pressure of your oxygen cylinder. A mismatch is a major safety hazard. |
| Outlet Pressure | Adjustable, e.g., 0-10 bar or fixed at 4.5 bar | Needs to align with the requirements of the connected equipment (ventilator, anaesthesia machine, etc.). |
| Flow Rate | 0-15 LPM (medical use); higher for industrial/lab | Determines the volume of oxygen delivered. Critical for patient therapy and process efficiency. |
| Materials | Brass, Chrome-Plated Brass, Stainless Steel | Essential for oxygen safety to prevent ignition. High-purity applications may require stainless steel. |
| Connections | DIN 477, CGA 540, Pin Index | Gas-specific fittings prevent accidental connection to the wrong gas cylinder. This is a crucial safety feature. |
| Certifications | MDR (EU) 2017/745, DIN EN ISO 10524-1 | Your guarantee that the device meets stringent European medical and safety standards. |
Understanding these parameters is the first step in selecting a regulator that is not only effective but, more importantly, safe for its intended environment.
When you're dealing with pure, high-pressure oxygen, your choice of materials is a life-or-death safety decision. While oxygen isn't flammable by itself, it's a powerful oxidiser, meaning it makes other things burn much more readily and intensely. This is exactly why you'll find that any high-quality Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch is built from very specific materials.
The absolute golden rule is that any material touching high-pressure oxygen must be "oxygen compatible". This is to prevent a nasty phenomenon called adiabatic compression ignition—basically, a fire sparked just by the rapid pressurisation of the gas. You can learn more about the unique chemical properties of oxygen and see why these safety measures are so critical.
To head off a potentially catastrophic mistake—like connecting the wrong gas regulator to a cylinder—a whole system of standardised, gas-specific connections was created. You can't just screw any old regulator onto any cylinder; the fittings are physically designed to make that impossible.
This is a global safety feature, though different regions use different systems:
At the end of the day, a medical oxygen pressure regulator isn't just a piece of metal hardware; it's a certified medical device. To be legally sold and used in clinics or labs in Europe, it must meet incredibly strict regulations that guarantee its quality, safety, and performance.
The big one is the Medical Device Regulation (MDR (EU) 2017/745), which lays down tough requirements for everything from design and manufacturing to testing and documentation. On top of that, the standard DIN EN ISO 10524-1 deals specifically with pressure regulators for medical gases. Seeing these certifications on a device is your assurance that it’s been properly tested and is fit for purpose. Choosing uncertified equipment is a gamble you should never, ever take.
It’s one thing to talk theory, but it’s in the real world where the true value of a Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch really hits home. These aren’t just add-on bits of hardware; they are the critical link in a chain that supports life-saving treatments, pioneering research, and the safeguarding of priceless biological samples. Their job changes dramatically depending on where you put them to work.
Take the high-pressure world of emergency medicine and hospital care. Here, these regulators are the unsung heroes, the steady heart beating at the centre of critical systems. They make sure patient ventilators and anaesthesia machines receive a constant, reliable flow of life-sustaining oxygen. The name of the game here is pure robustness and absolute dependability, whether that’s in a sterile operating theatre or the back of a speeding ambulance.
But the story doesn't end with direct patient care. In highly specialised fields, the demand shifts from brute strength to delicate control, where the regulator’s role becomes one of finesse and unwavering stability.
In fertility clinics, for example, these regulators are quietly working to maintain the perfect, stable atmosphere inside incubators. For embryos to develop successfully, a consistent and pure gas supply is completely non-negotiable. Even the slightest hiccup in gas pressure could jeopardise weeks of incredibly sensitive work.
This need for stability is even more pronounced in cutting-edge biobanks and cell therapy labs. Here, a Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch is tasked with supplying a precise, low-pressure stream of gas for cryogenic freezers. This creates the perfect preservation environment for invaluable biological samples, protecting everything from stem cells to tissue grafts for future use.
At its core, the job is always the same: control pressure safely and accurately. But the specifics—whether you need ruggedness for an emergency call-out or ultra-high purity for pharmaceutical research—are what determine the right regulator for the task.
The environment where a regulator operates completely changes the feature set you need. A device built for an ambulance bouncing down the road is a world away from one used in a sterile cleanroom.
Looking at these different scenarios makes it obvious why a "one-size-fits-all" approach to choosing a Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch just doesn't work. Safety and success hinge on matching the device’s capabilities to the job at hand. This is especially true in broader public health, where reliable equipment is vital.
In Germany, for instance, there's been a surge in demand for medical oxygen equipment, including the Druckminderer Sauerstoff medizinisch. This is largely driven by the rise in chronic respiratory diseases, often exacerbated by air pollution. Portable medical oxygen concentrators captured a massive 54.75% revenue share in 2023, valued for their lightweight designs and tech that guarantees safe, regulated oxygen delivery. These units are often paired with precise pressure regulators to hold therapeutic pressures between 0.5-4 bar—a critical factor for patient safety during home therapy. You can dig deeper into the data on the German oxygen concentrator market and its drivers.
This trend just goes to show how crucial high-quality, dependable oxygen delivery systems have become, both in hospitals and at home. Picking the right regulator isn't just a technical choice; it’s a fundamental step in ensuring good patient outcomes and maintaining the integrity of scientific research. It is the bridge between a high-pressure gas cylinder and a safe, successful application.
Choosing the right druckminderer sauerstoff medizinisch can feel daunting, but it doesn't have to be. By breaking it down into a few logical steps, you can confidently pick the perfect device for your needs. The whole process really boils down to ensuring the regulator’s capabilities are a perfect match for the job you need it to do—guaranteeing safety, accuracy, and reliability every single time.
It all starts with a simple question: what is this regulator's main purpose?
Answering that question lays the groundwork for every other decision. A regulator needed for a first responder in an emergency has wildly different demands than one used for cryopreservation in a sterile lab. The environment, the level of precision required, and the day-to-day operational stresses will dictate your choices from here on out.
This flowchart can help you visualise the decision-making process based on your primary application, whether it's direct patient care, delicate laboratory work, or industrial cryogenics.
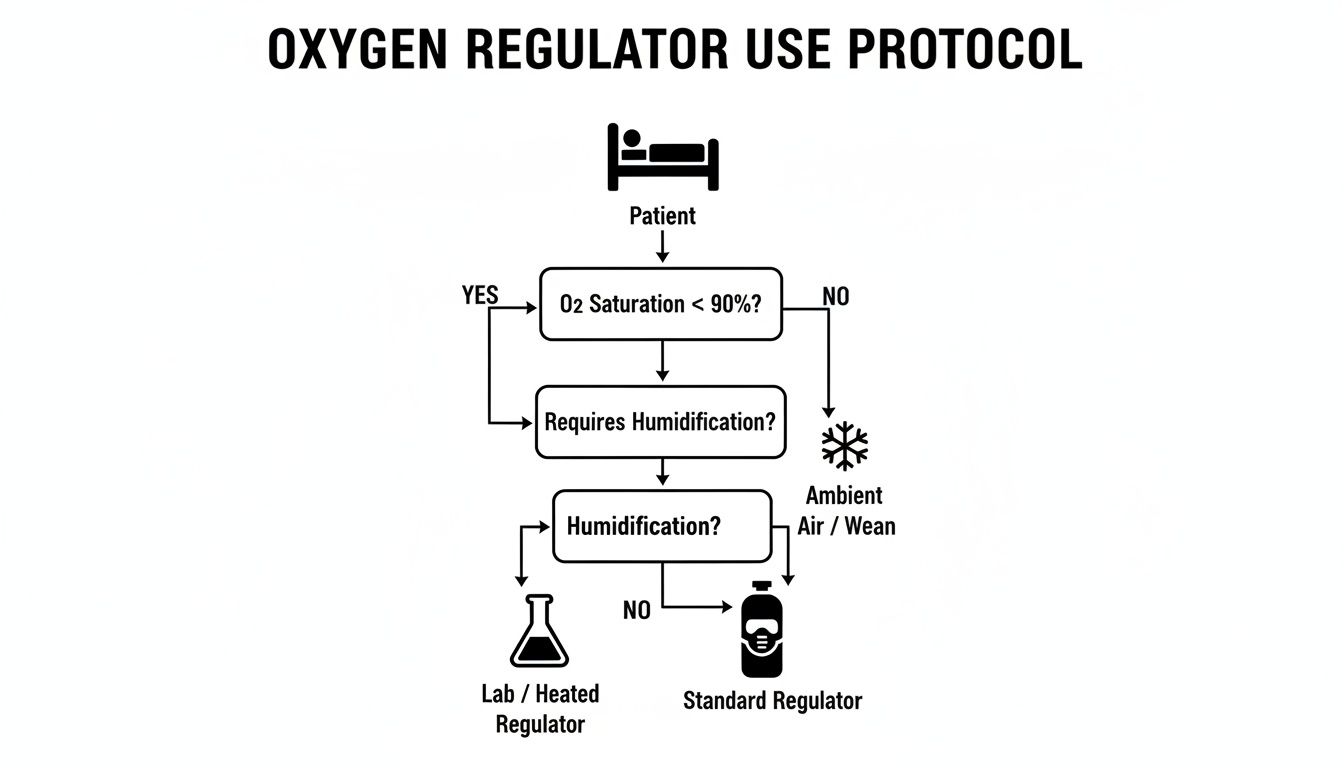
As the chart shows, every field—be it clinical, research, or industrial—has its own set of non-negotiable demands that point you toward specific regulator features and designs.
Once you've pinpointed the application, it's time to get into the technical details. This is where you move from the "what" to the "how," nailing down the exact performance metrics your regulator must deliver. Getting this part right is absolutely critical for both function and safety.
Focus on these three core specifications first:
Knowing your gas cylinders is also key to preventing dangerous mix-ups. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on the colour coding of gas cylinders.
Where the regulator will be used adds another important layer to your decision. A standard regulator might work flawlessly in a climate-controlled hospital room but could fail or become a hazard in more demanding conditions.
A perfect example is MRI compatibility. A standard brass or steel regulator is a definite no-go—it's ferromagnetic and poses a massive safety risk in an MRI suite. For these environments, you must use a regulator made from non-ferromagnetic materials like specific aluminium alloys, and it must be clearly marked as "MR Conditional."
Selecting the right regulator is not just about meeting a single technical specification. It's about finding a device where the flow rate, pressure, materials, and certifications all align perfectly with the demands of the application and its environment.
With your requirements clearly defined, you can now start comparing specific models. Laying everything out in a table is a great way to see how different regulators stack up against your checklist.
To simplify the process, this table breaks down the key considerations for common applications, helping you align your needs with the right type of regulator and features.
| Application | Key Requirement | Recommended Regulator Type | Cryonos Solution Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital/Clinical Use | Precision patient dosing, reliability | Diaphragm-style, two-stage for stability | Medically licensed products meeting MDR standards |
| Biobanks/Cryopreservation | Stable pressure for freezers, purity | Two-stage, stainless steel for purity | Gold-standard evaporation rates for supply consistency |
| Emergency Services | Durability, ease of use in the field | Piston-style, rugged construction | Robust designs with long maintenance intervals |
| Pharmaceutical Labs | Ultra-high purity, no contamination | Stainless steel, cleanroom assembled | High-purity compatible components |
By methodically working through these steps—defining the application, specifying technical needs, considering the environment, and comparing models—you can confidently select the ideal druckminderer sauerstoff medizinisch. This structured approach removes the guesswork and ensures the regulator you choose delivers the safety and performance you depend on.
Properly handling a druckminderer sauerstoff medizinisch is about more than just getting it to work—it's about keeping everyone safe and making the equipment last. Think of it this way: clear best practices for installation, routine maintenance, and safety checks are what make your oxygen regulator a reliable, secure link in your operational chain. This holds true whether you're in a busy clinic, a high-tech lab, or an industrial setting.

It all starts with a meticulous installation. Even a tiny mistake here can spiral into bigger problems down the line, from inaccurate gas delivery all the way to dangerous leaks. By taking a structured approach from the very beginning, you create a secure and efficient connection that sets the stage for safe operation every time.
Getting the installation right is actually pretty straightforward when you follow a precise sequence of steps. This ensures the regulator is seated correctly, sealed tightly, and ready for service.
Regular checks are your first line of defence. They're vital for catching small issues before they snowball into serious safety hazards. A simple but consistent inspection routine is the best way to prevent equipment failure. Part of this routine involves confirming the safe storage of your oxygen cylinders, a topic we cover in our detailed guide on oxygen cylinder storage.
Your routine checks should always include:
The single most important rule in oxygen handling is to never allow oil, grease, or any petroleum-based lubricant to come into contact with any part of the regulator or cylinder. In an oxygen-rich environment, these substances can ignite violently, causing a serious fire or explosion.
Keep an eye out for common issues like fluctuating pressure readings or an incorrect flow rate, as they often point to simple fixes. If the pressure is jumping around, it might suggest an internal issue or, more commonly, a nearly empty cylinder. If the flow seems off, it could be a blockage or a faulty flowmeter.
If basic troubleshooting doesn't solve the problem, the unit must be taken out of service immediately and inspected by a qualified technician. Sticking to these guidelines ensures your equipment remains reliable and, most importantly, safe for every single use.
When you're working with a druckminderer sauerstoff medizinisch, a few questions always come up. Getting straight answers is key to using this vital equipment safely and correctly. Let's walk through some of the most common queries we hear.
Think of this as a quick guide to everything from routine upkeep to the science behind why these devices are built the way they are. Understanding these points will help you ensure safety and peak performance every time.
There’s no single, universal "use by" date for a regulator. The right replacement schedule really depends on the manufacturer's recommendations, how heavily it's used, and the environment it lives in.
As a solid rule of thumb, plan for a professional inspection and full service at least every 5 years. But here's the critical part: if a regulator shows any visible damage, serious wear and tear, or isn't performing right, it needs to be taken out of service and replaced immediately. No ifs, ands, or buts. In high-demand settings like hospital wards or emergency services, more frequent checks are an absolute must.
Absolutely not. This is a hard-and-fast rule you should never, ever break. Industrial oxygen regulators must not be used for any medical purpose.
Medical-grade regulators are built under incredibly strict standards for cleanliness, materials, and assembly. This is all to guarantee that no harmful contaminants can get into the gas a patient breathes.
Medical devices must be certified under demanding regulations like the EU's Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Using an industrial unit for a medical application introduces a massive, unacceptable health risk and completely sidesteps the safety protocols designed to protect patients.
The number one reason to choose a two-stage regulator is its incredible pressure stability. A single-stage model does the job in one step, but as the cylinder pressure drops, the outlet pressure can creep up slightly. It's a known phenomenon called the supply pressure effect.
A two-stage regulator, on the other hand, drops the pressure in two separate steps. This clever design effectively buffers the final output from any pressure swings in the cylinder. The result? A rock-solid, consistent flow from the moment you open a full cylinder until it’s nearly empty. This level of precision is non-negotiable for sensitive lab instruments and long-term medical therapies.
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is the go-to material for oxygen regulators for one huge reason: it’s highly resistant to ignition in an oxygen-rich, high-pressure environment. That makes it an exceptionally safe choice for this specific job.
But its safety profile is just the start. Brass is also tough, resists corrosion, and is easy to machine into the precise, complex shapes a regulator requires. While you might see stainless steel in some ultra-high-purity applications, brass strikes the perfect balance of safety, reliable performance, and cost-effectiveness for most medical and lab oxygen systems. You'll often see it chrome-plated, which adds extra protection and makes it easier to clean.
For state-of-the-art cryogenic and gas handling solutions that meet the highest medical and safety standards, trust Cryonos GmbH. Explore our comprehensive portfolio of medically licensed equipment, backed by decades of expertise. Visit https://www.cryonos.shop to find the right solution for your laboratory or clinic.